Misc Articles
Muscle Physiology – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 21, 2011 | 6:05 am | 0 Comment
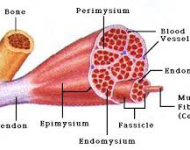
Muscle tissue – (myo, mys, sarco) -skeletal – striated, voluntary -smooth – visceral, nonstriated, involuntary -cardiac – heart, striations, involuntary Skeletal Muscle Functions -movement -cardiac – blood -smooth – peristalsis -skeletal – gross movements -posture / stabilize joints -generates heat (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || more...
Endocrine Disorders – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 20, 2011 | 7:12 am | 0 Comment
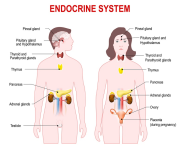
Hormones are chemical messengers. They are a major way in which our body communicates with itself. If our messages are unable to do their job, i.e. too much *hypersecretion or too little *hyposecretion, serious problems can result. The following are common endocrine disorders. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) -hyposecretion / hypoactivity of insulin -without insulin, glucose more...
Function of Kidneys overview – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 18, 2011 | 9:38 am | 0 Comment
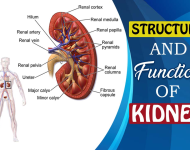
Urinary System I. Organs A. 2 Kidneys 1. Major excretory (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({ google_ad_client: "ca-pub-4816419112981891", enable_page_level_ads: true }); organs 2. Filter blood 3. Eliminate nitrogenous waste a. Creatinine – muscle metabolism, creatine breakdown b. Urea – amino acid metabolism c. more...
Physiology of Liver – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 18, 2011 | 9:28 am | 0 Comment
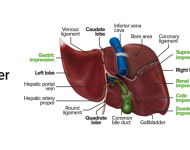
The liver is an amazing organ. A single hepatocyte (liver cell) can conduct over 1000 metabolic reactions. Here is an overview of some of the highlights of the liver. 1. Metabolic Regulation -blood leaving digestive tract enters hepatic portal system and flows to the liver -regulates composition of circulating blood (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || more...
Nutrition – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 17, 2011 | 9:07 am | 0 Comment
Macromolecules -- Energy Yielding Nutrients I. 3 Energy Yielding Nutrients (Macromolecules) A. Carbohydrates B. Proteins C. Lipids II. Carbohydrates A. Composed of Carbon and Water (CH2O)n B. Simple Sugars 1. Monosaccharides and Disaccharides (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({ google_ad_client: "ca-pub-4816419112981891", more...