Flu vs Cold – outline notes
Call Us Now
Get the Best CPR Class in St. Louis Today!
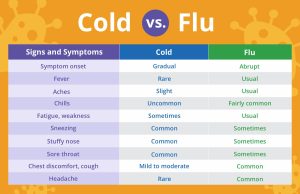
I. Common Cold
A. Causative agent – virus
1. 5 different viruses – over 100 strains
B. Symptoms
1. Respiratory infection
a. Sore throat, sneezing, runny nose, congestion (thick yellow
mucus)
C. Cannot catch a cold from:
1. Draft, wet hair, sudden drop in temperature
D. No vaccine
II. Flu (Influenza)
A. Causative agent – virus
1. Strains – evolve very rapidly
a. Type A – most common, most serious epidemics
b. Type B – epidemics, but less severe symptoms than A
c. Type C – no epidemics
2. Symptoms
a. Extreme exhaustion
b. High fever
c. Headache
d. Body / muscle aches
e. Cough
f. Does not affect stomach or intestines
3. Spread by
a. Catch by contact with mucous membranes – eyes, nose, mouth
b. Virus is shed by mucus of infected people
c. Passes thru air or contact with contaminated object (fomite)
1) Hand to face — most common way to contract virus
2) Wash hands
4. Pandemics
a. 1918 Spanish flu
1) Over 20 million deaths worldwide; 500,00 in US
b. 1957 and 1968 Asian and Hong Kong flu
c. 2003 Avian flu outbreak
1) Usually flu virus moves from chickens to pigs, then to
humans
5. Flu complication – secondary infection by bacteria
6. Vaccine
a. A and B viruses expected to circulate
III. Treatments
A. Rest
B. Fluids
C. Gargle salt water
D. Steam to reduce congestion
E. Medicines
1. Antihistamines – runny nose, sneezing, however makes mucus thicker
2. Decongestants – relieve sinus pressure and stuffy nose
3. Analgesics
a. Acetaminophen, aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen
4. Cough suppressants
a. Dextromethorphan






