Introduction to Pediatric CPR and PALS Guidelines
Saving a child’s life in a cardiac emergency demands swift and precise action. In the crucial moments of pediatric cardiac arrest, knowing the correct compression-to-ventilation ratio is paramount for effective CPR. Pediatric Advanced Life Support, or PALS, provides the foundational guidelines for these life-saving interventions. This article delves into the core principles of CPR compression ratios, specifically exploring the differences between the 15:2 and 30:2 ratios, and outlining when each is most appropriate. Understanding these distinctions is not merely an academic exercise; it is a critical skill for healthcare providers and lay rescuers alike, directly impacting the quality of care and the potential for positive outcomes in pediatric emergencies.
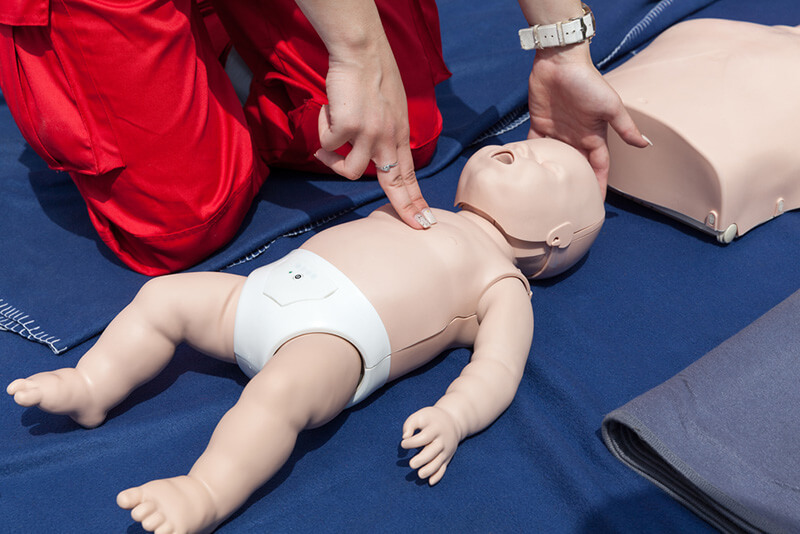
Fundamentals of CPR Compression-to-Ventilation Ratios
The essence of effective CPR, whether for adults or children, lies in maintaining adequate blood flow and oxygenation to vital organs. Compression-to-ventilation ratios define the number of chest compressions delivered for every two rescue breaths. While the fundamental mechanics of compressions and ventilations remain consistent, the physiological differences in pediatric patients necessitate a tailored approach.
Physiological Differences in Pediatric Patients
Unlike adults, whose cardiac arrest often stems from a primary cardiac event, children typically experience cardiac arrest secondary to respiratory failure or shock. This fundamental difference underscores the increased emphasis on ventilation in pediatric CPR and explains why different ratios are recommended depending on the specific circumstances.
The 15:2 Compression Ratio – Healthcare Provider Standard
When faced with a pediatric cardiac emergency, especially in a healthcare setting with multiple trained individuals, the 15:2 compression ratio becomes the gold standard. This ratio signifies 15 chest compressions followed by two ventilations.
Healthcare Setting Applications
The primary advantage of the 15:2 ratio lies in its ability to provide more frequent ventilations, which is crucial given the common respiratory origins of pediatric cardiac arrest. In a two-rescuer CPR scenario, the coordinated effort allows one rescuer to focus on delivering high-quality chest compressions while the other simultaneously prepares and delivers breaths, minimizing interruptions and optimizing oxygen delivery to the child’s lungs and tissues.
Implementation Techniques for 15:2 Ratio
Proper technique for this ratio involves precise hand placement—typically two fingers for an infant or one or two hands for a child, depending on size—ensuring adequate compression depth and rate, and seamlessly integrating ventilations between compression cycles.
Coordinated Team Approach
Healthcare providers, with their advanced training and access to specialized equipment, are well-equipped to implement this coordinated team approach.
The 30:2 Compression Ratio – Single Rescuer Approach
Conversely, the 30:2 compression ratio is primarily recommended for single-rescuer CPR scenarios, particularly in lay rescuer situations or when advanced airway management is not immediately available. This ratio, consisting of 30 chest compressions followed by two ventilations, mirrors the standard adult CPR ratio, making it easier for individuals trained in basic life support to recall and implement.
Lay Rescuer Scenarios
While the 15:2 ratio prioritizes more frequent ventilations, the 30:2 ratio emphasizes minimizing interruptions in chest compressions, which is vital for maintaining blood flow, especially when only one rescuer is present.
Benefits of the 30:2 Approach
A single rescuer must balance the delivery of effective chest compressions with the provision of ventilations, and the 30:2 ratio simplifies this process, allowing for a more continuous flow of compressions.
Consistency with Adult CPR Guidelines
This consistency with adult CPR guidelines also aids in the broader dissemination of CPR training among the general public, fostering a more prepared community capable of responding to emergencies.
Decision-Making Factors for Compression Ratio Selection
The decision of which compression ratio to employ hinges on several critical factors. The most immediate consideration is the number of rescuers present. In a two-rescuer setting, the 15:2 ratio allows for a more efficient and coordinated approach, with one rescuer focusing on compressions and the other on ventilations. This team coordination is essential for optimizing both blood flow and oxygenation. However, in a single-rescuer situation, the 30:2 ratio is more manageable, as it streamlines the process for one individual.
Training Level and Certification
Beyond the number of rescuers, the training level and certification of those involved also play a significant role. Healthcare providers, with their advanced training and access to specialized equipment, are often prepared to utilize the 15:2 ratio effectively, whereas lay rescuers are more commonly trained in the 30:2 ratio due to its simplicity and consistency with adult CPR.
Patient-Specific Factors
Patient-specific factors also heavily influence the choice of ratio. The age of the child is crucial; while the principles apply to both infants and children, the technique and depth of compressions will vary.
Suspected Cause of Cardiac Arrest
The suspected cause of cardiac arrest is another vital consideration. If respiratory issues are the primary concern, as is often the case in pediatric emergencies, then a ratio that provides more frequent ventilations, like 15:2, might be preferred if sufficient rescuers are available.
Equipment and Setting Considerations
Furthermore, the presence of an advanced airway, such as an endotracheal tube, can significantly alter the approach, as continuous compressions can then be delivered independently of ventilation. For a deeper understanding of pediatric basic life support, exploring resources on infant CPR techniques can be beneficial.
American Heart Association Guidelines and Evidence
The American Heart Association (AHA) continually updates its guidelines for CPR and emergency cardiovascular care based on the latest scientific evidence. These recommendations provide the authoritative framework for selecting appropriate compression ratios.
Quality Metrics and Performance Standards
The AHA emphasizes the importance of high-quality CPR, regardless of the ratio used, focusing on adequate compression depth and rate, full chest recoil, and minimizing interruptions. Scientific evidence supporting the various ratio selections is robust, derived from extensive research and clinical observations.
Performance Indicators and Assessment
Quality metrics and performance indicators are also crucial in assessing the effectiveness of CPR delivery, encouraging continuous improvement in training and implementation. Staying abreast of the latest AHA guidelines is essential for all who might be called upon to perform CPR.
Practical Implementation and Training
Understanding the nuances between the 15:2 and 30:2 compression ratios is fundamental to providing effective pediatric CPR. While the 15:2 ratio is preferred in two-rescuer, healthcare provider settings due to its emphasis on more frequent ventilations, the 30:2 ratio remains vital for single-rescuer and lay rescuer situations, prioritizing continuous compressions.
Quality Assurance in Pediatric CPR
The ultimate goal in any pediatric cardiac arrest scenario is to deliver high-quality CPR that maximizes the chances of survival and positive neurological outcomes. This means focusing not just on the chosen ratio, but on the quality of compressions, the adequacy of ventilations, and the minimization of interruptions.
PALS Certification Standards
Regular training and consistent practice are indispensable for maintaining proficiency in these life-saving skills. For healthcare providers, upholding PALS certification is not merely a professional requirement but a profound commitment to saving young lives.
Conclusion and Call to Action:
Understanding the key differences between the 15:2 and 30:2 compression ratios in Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) is crucial for any healthcare provider involved in pediatric emergencies. These ratios are not interchangeable; each serves a specific purpose depending on the number of rescuers and the age of the patient. Mastering when and how to apply these techniques can greatly improve the chances of survival and recovery for infants and children during cardiac arrest.
At CPR St. Louis, we ensure that all our students receive hands-on, practical training that brings clarity to these life-saving protocols. Whether you’re new to pediatric resuscitation or need a refresher, our certified courses make complex concepts easy to understand and apply.
Take the next step toward excellence in emergency care. Enroll today in a CPR certification St. Louis or PALS certification St. Louis course and gain the confidence to act decisively when every second counts.





