Browsing Posts of Author
Bone Formation and Calcium Regulation | Endocrine
By CPR St. Louis at September 23, 2011 | 10:36 am | 0 Comment
Bone formation via Endochondral ossification 1. Most bones 2. Mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondroblasts and produce hyaline a. Interstitial and appositional growth 3. Perichondrium – chondrogenic cells; C.T. surrounds hyaline a. Perichondrium becomes periosteum (osteoblasts) due to increased blood supply 5 Steps of Endochondral Bone more...
Bone Physiology – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 23, 2011 | 10:28 am | 0 Comment
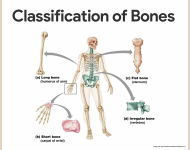
I. Basic Functions of Bones A. support – shape and form B. storage – minerals (Ca2+, PO43-) and lipids (yellow bone marrow) C. blood cell production – red bone marrow D. protection E. movement (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({ google_ad_client: "ca-pub-4816419112981891", enable_page_level_ads: true }); II. more...
Nervous System Physiology – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 22, 2011 | 6:59 am | 0 Comment
Nervous System and Endocrine System = maintain homeostasis, control Neural Tissue Cells – Neuroglia and Neurons Neuroglia (glial cells) – supporting cells (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({ google_ad_client: "ca-pub-4816419112981891", enable_page_level_ads: true }); -CNS – 4 types 1. Ependymal cells -line more...
Muscle Physiology – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 21, 2011 | 6:05 am | 0 Comment
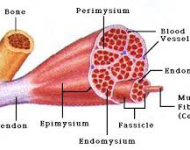
Muscle tissue – (myo, mys, sarco) -skeletal – striated, voluntary -smooth – visceral, nonstriated, involuntary -cardiac – heart, striations, involuntary Skeletal Muscle Functions -movement -cardiac – blood -smooth – peristalsis -skeletal – gross movements -posture / stabilize joints -generates heat (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || more...
Endocrine Disorders – outline notes
By CPR St. Louis at September 20, 2011 | 7:12 am | 0 Comment
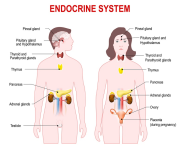
Hormones are chemical messengers. They are a major way in which our body communicates with itself. If our messages are unable to do their job, i.e. too much *hypersecretion or too little *hyposecretion, serious problems can result. The following are common endocrine disorders. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) -hyposecretion / hypoactivity of insulin -without insulin, glucose more...